43% of retail customer experiences start with a search engine. That means if you want to sell products, spread the word about a cause, get people to your event, attract readers for your blog, people will most likely find you through search. Thus, you need a strong presence on search engines and that is achieved through search engine optimization (SEO).
The trouble is, everybody and her cat are using SEO to improve their online reach. But it doesn’t mean they’re using it effectively or even correctly. If you gain a comprehensive understanding of all facets of SEO, you can use it to your advantage. And it will pay off. 60% of marketers say their inbound marketing efforts, such as content and SEO, bring in the highest quality leads.
Learn SEO in 6 Easy Steps
In this post, you’ll learn the fundamentals of SEO on which to build an impactful strategy. Plus, we’ll guide you to the tools and resources that’ll assist you greatly on your SEO journey.
- Understand How Search Engines Work
- Master Google’s Ranking Factors
- Learn How to Do Keyword Research
- Get to Grips with Technical SEO
- Discover Link Building
- Stay Up-To-Date with the Right Resources
Step 1: Understand How Search Engines Work
When somebody performs a search related to your content or business, you want your page to appear at the top of the list. The goal of SEO is to keep moving your pages up the list of search engine results.
We’ll focus on how to improve your results on Google, as other search engines, such as Bing, don’t come anywhere near Google’s massive market share of 92.12%.
Google sends out crawlers (bots) that consume all of the content on the web. It indexes your pages, in other words, adds your pages to a database. It also ranks your website and pages based on a number of factors in order to provide the best answers for its users’ searches. When your page is a good match for what a user searches, Google is then able to produce your page from its database. Hence, the first vital step of SEO is to make sure Google can find and crawl your site easily.
It helps to have a clear site architecture. In other words, your site must be laid out in a way that’s easy for users and Google’s bots to navigate. Your home page links out to category pages and these category pages link out to relevant sub-pages. It may look something like this:
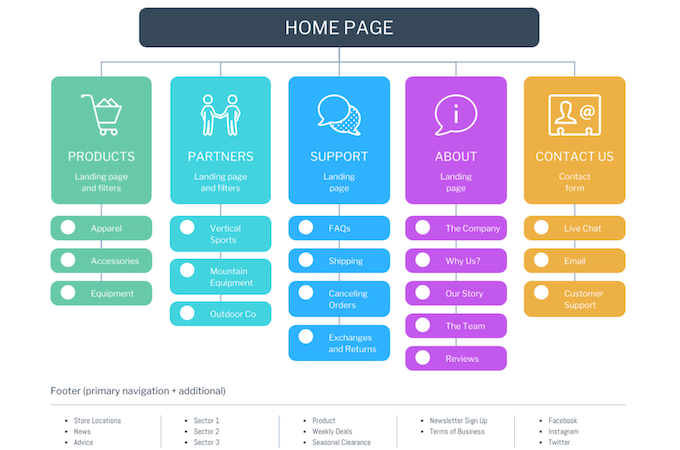
Once you have a good site architecture in place, generate a sitemap, which is essentially a list of links detailing this structure along with other important information, such as when each page was last updated. Use an SEO plugin such as All in One SEO or Yoast to generate the sitemap for you.
Then, submit your sitemap to Google Search Console. This ensures Google has the most up-to-date view of your site and its architecture.
Step 2: Master Google’s Ranking Factors
Ranking factors are characteristics or metrics Google uses to assess the quality and relevancy of your web pages for a given search. These determine what number you place in the search engine results pages (SERPs). Experts believe there are around 200 known ranking factors.
Don’t be daunted by this or get too bogged down with individual ranking factors. All you need to know is that in the current SEO landscape, Google wants to provide comprehensive results from trustworthy sources, and they want users to have a good experience with your site. These are the key concepts for you to focus on to improve SEO.
Search Engine Journal names the following as the top ranking factors (in no order):
- High-quality content – Content must be up-to-date, relevant to the search in question, and engaging, keeping the user on the page.
- Mobile-first – Most searches are done on mobile, so your website’s design and usability must put the mobile experience first.
- Page experience – Your site must be easy-to-navigate, secure, and easy to interact with.
- Page speed – When pages load slowly, users get frustrated and leave a site, which obviously doesn’t represent a good user experience so its best to ensure page load speeds are fast.
- On-page optimization – Pages are laid out in a clear and easy-to-follow structure. Plus, all the behind-the-scenes, technical SEO is in order (we’ll cover this in greater depth later).
- Internal links – The way you link from one page to the next has a structure, makes sense, and flows well for users navigating your site.
- External links – When sites that have authority link to yours it acts as a trust signal for Google and a sign that your content displays depth and quality.
Step 3: Learn How to Do Keyword Research
Keyword research means finding and analyzing the terms, phrases, and questions users search for on Google. With an SEO tool such as Semrush or Ahrefs, you can find out the keywords people search for most, how often these keywords are searched, further related keywords, how much competition there is for these keywords, and more. This data informs which keywords you need to target as well as your wider SEO strategies.
All you need to do is enter broad terms or topics into Semrush’s Keyword Magic tool and you’ll discover the best keyword opportunities to go after:
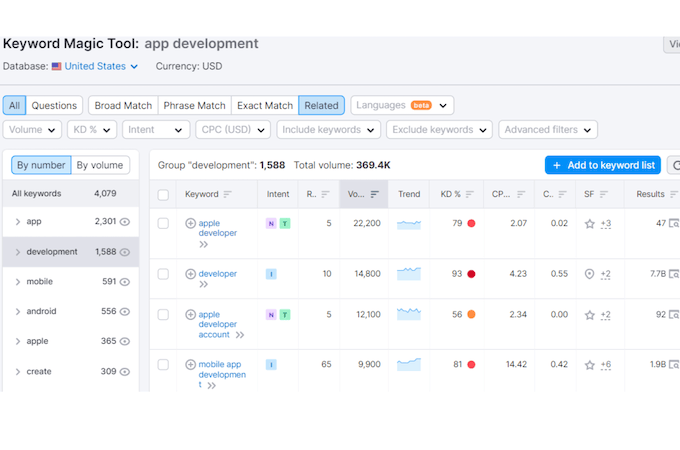
Here you can see that popular search terms related to “app development” are “apple developer” and “mobile app development”. The volume column shows the number of monthly searches for the keyword, while the column labeled KD % gives a keyword difficulty score out of 100.
One keyword strategy is to target so-called long-tail keywords. These keywords have a lower search volume but are easier to rank for. As you build up your rankings for these lower-volume keywords, it becomes easier to rank for the higher-volume keywords.
Another popular keyword strategy is to target keyword clusters with content. First, you create a broad pillar post targeting a high-volume keyword. Then cover subtopics targeting long-tail keywords, and link out from the pillar post to your subtopics.
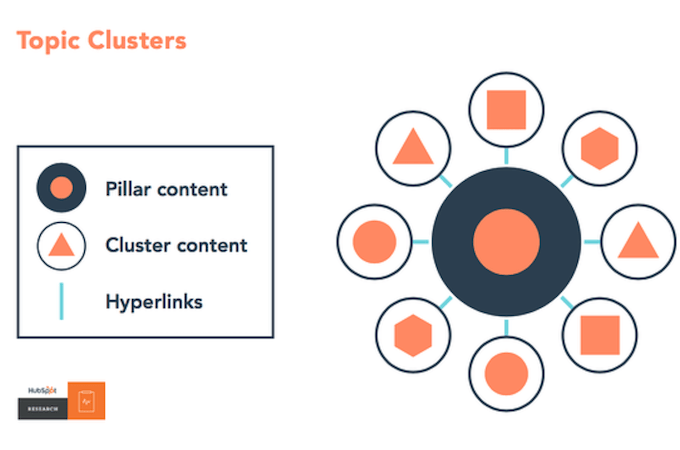
To give you an example, your pillar content may target “mobile app development,” while cluster content targets “mobile app development software,” “mobile app development cost,” and so on.
This essentially proves to Google that your site is the go-to resource for topics related to a keyword as it covers it so comprehensively. You are the expert, so you deserve a higher ranking in the search engine results pages.
Step 4: Get to Grips with Technical SEO
There are two fundamental sides to SEO. One involves keywords and content; the other is technical SEO. The latter represents the way you optimize your website to make it easier for Google to crawl it and understand it. It’s important because, as you’ve seen, aspects of technical SEO influence search engine rankings.
Here are some of the most important technical optimizations:
- Use HTTPS – This encrypts the connection to your website and makes it super secure. Google Chrome even flags sites that don’t use it as unsafe.
- Improve core web vitals – These break down elements of your website speed, such as the time it takes for the largest element to load, e.g., images and video, or the time it takes for your site to become interactive, e.g., when a user can click on something.
- Fix broken pages and links – These produce an error page when a website visitor clicks on them so represent a bad user experience to Google.
- Add structured data – This is code you add to your pages that make the way Google displays search results more useful. For instance, structured data adds a star rating or telephone number underneath your link on the search engine results page.
- Fix crawl errors – Find and fix pages that Google is unable to crawl, e.g., when there’s a duplicate page Google’s crawlers aren’t sure which to index.
Make finding and fixing technical SEO issues easier with an SEO tool, such as Google Search Console or Semrush’s Site Audit tool.
Step 5: Discover Link Building
Link building involves using marketing tactics to encourage bloggers, influencers, thought leaders, and influential websites to link back to your site. Backlinks are thought to be one of Google’s top three ranking factors. The more links you build, the more trust and authority are passed onto your site, increasing search engine rankings.
A good starting point for link building is to analyze your competitor’s backlink profiles (list of links). Semrush’s Backlink Gap tool shows where your backlinks intersect with multiple competitors and what your best link building opportunities are for outranking these competitors.
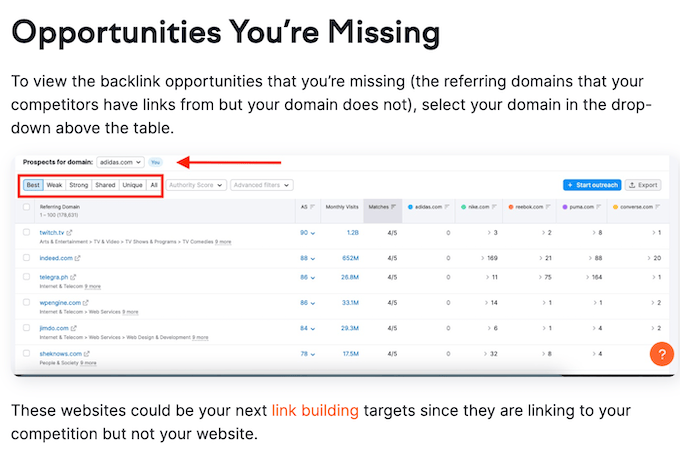
The sites listed represent your link prospects. There are multiple strategies you can use to also acquire links on those sites. For instance, you may offer to write a guest post for the site that includes links back to your site. Or you may find any broken links on their site and offer your own content as a replacement.
Having something worth linking to is the foundation of any link building strategy. Prospects are unlikely to link to your homepage. They may, however, be willing to link to a useful resource, in-depth content, original research, or infographic on your site.
Be sure to send personalized emails to your link prospects. Influential website owners receive multiple requests daily. So you have to prove that you have something that is genuinely valuable and genuinely a good match for their site. Show you’re not simply sending a bulk email to every other person in your niche.
Step 6: Stay Up-To-Date with the Right Resources
The rules and best practices surrounding SEO change often. Google tweaks the algorithms it uses to rank websites regularly—some say 12 times per day on average.
But don’t worry too much. The core principles that represent the modern SEO landscape are unlikely to change any time soon. These are the need to prove that your site is trustworthy, easy to navigate, has lots of quality content, and so on. In other words, what you should be doing to provide a great experience for your audience anyway.
But, it is important to keep up-to-date with any news coming from Google that may affect your SEO performance. Also, to continue to learn the best strategies and techniques to outrank your competitors.
Here are some handy resources for continued learning on SEO:
- Google Search Central – It has a bunch of guides both basic and advanced by Google staff and experts. There’s also a blog on which Google releases any important news regarding search.
- SEO news sites – Sites such as Search Engine Land and Moz are extremely quick to share and comment on new SEO developments.
- SEO blogs – These kinds of sites are more likely to offer comprehensive guides to SEO, step-by-step walkthroughs, tool reviews and comparisons, and so on. Take a look at Quick Sprout’s SEO guides for more of our expert advice.
- Online courses – There are a couple of places you can take free SEO courses from experts with accreditation at the end of them, for instance, Semrush Academy and Google Skillshop.
Final Thoughts About Learning SEO
Marketing professionals and brands of all sizes need to understand SEO. Most online journeys begin with a Google search, after all. There are some fundamental concepts you need to comprehend and strategies to master if you hope to learn SEO.
These are the basics of how search engines work along with what Google considers the most important ranking factors. If you know how to perform keyword research, do technical SEO, and build links you’re on your way to grasping SEO. Yet, since the SEO space is ever-evolving you must stay up to date with what’s new from Google and the SEO industry in order to keep doing SEO effectively.
